AWS Recipe: Using System Session Manager
(instead of key pairs for connecting to EC2 instances)
What is AWS Systems Manager Session Manager?
Session Manager is a fully managed session manager of the AWS Systems Manager service. It frees you of opening ports like SSH in most scenarios and enables a more centralized control of accessing your services/instances.
Scenario Use Cases:
- Not using key/pairs- You're labbing for an AWS certificate, and the thought of losing or managing your keys stresses you out.
- Maybe you want an alternative to using a SSH client and just want to stick with the Console as much as possible.
- You're on a team and want the ability to revoke access to another developer if needed, avoiding retaliation-related nightmare scenarios.
Basic Step-by-Step Guide
1. Launching an example EC2 instance with appropriate role
Here I'm launching an EC2 instance called `example_server` (using an Ubuntu quick start and instance type of t2.micro) and scrolling down to Advanced Details:
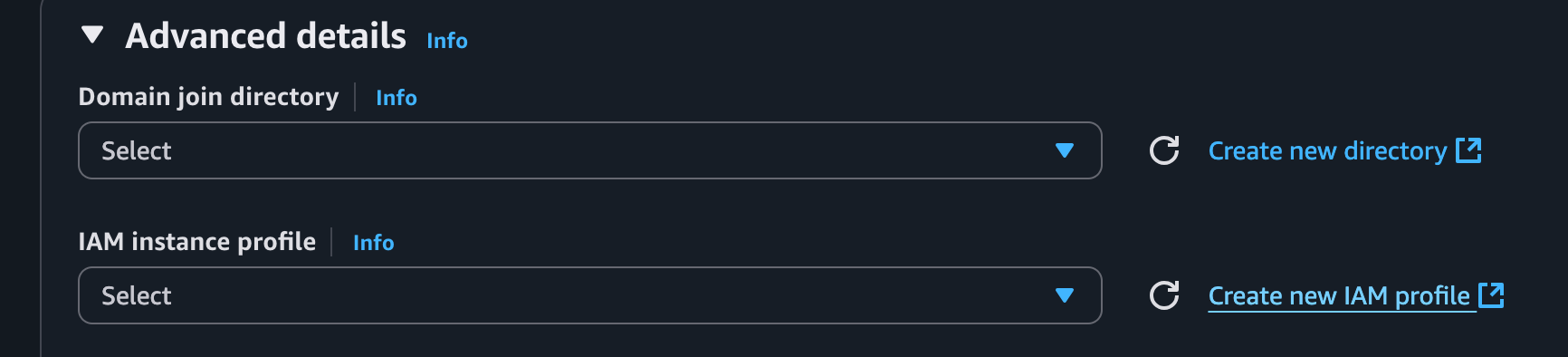
If you already created the EC2 instance you can edit this later through Actions > Security > Modify IAM Role.
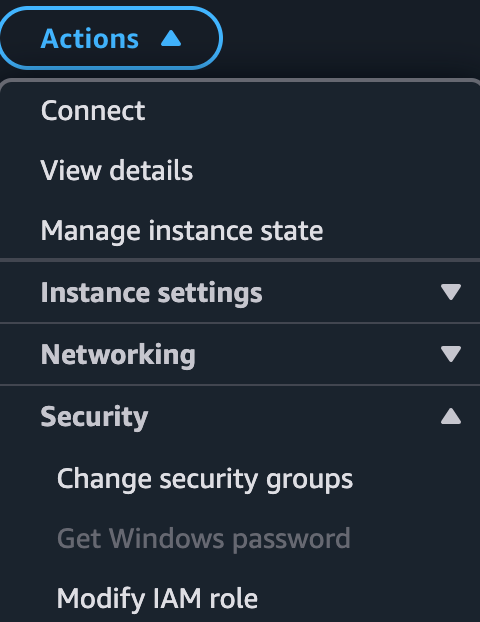
2. Creating the IAM role
An IAM role is needed for access.
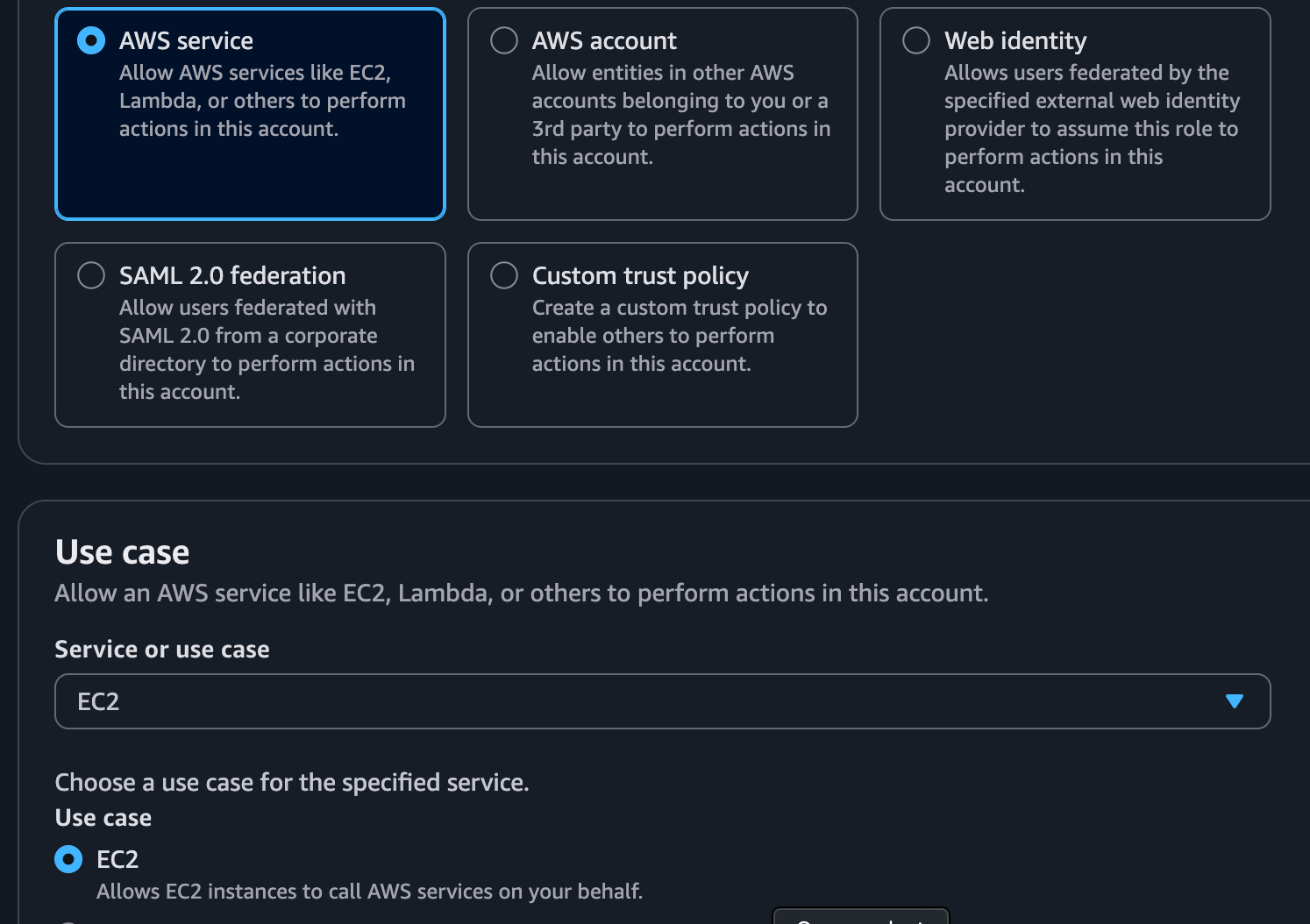
3. Applying appropriate permissions to role
The most straightforward way to allow full access to an instance is to select the built-in policy AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore
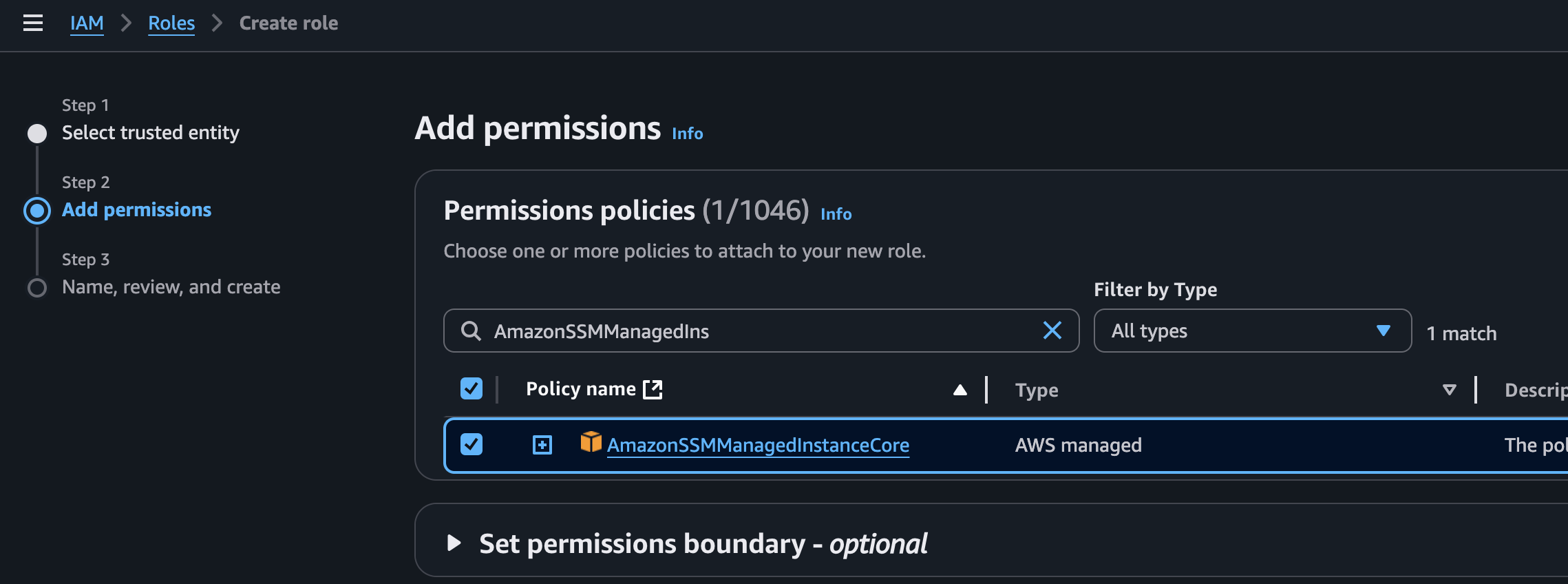
📝 Note: Make sure as of 2025 that `AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore` policy is selected. Some older tutorials may still show `AmazonEC2RoleforSSM` but it will be deprecated in the near future.
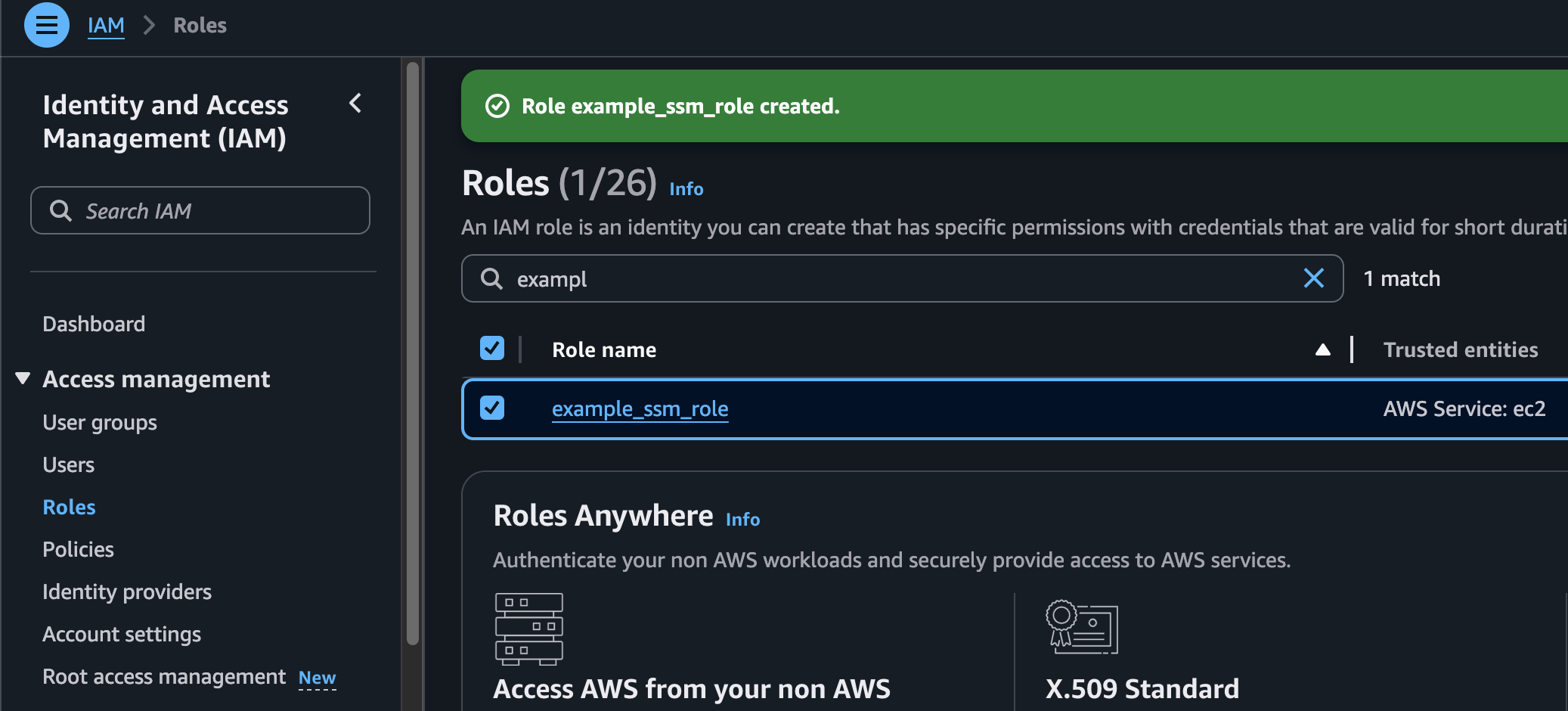
4. Role created
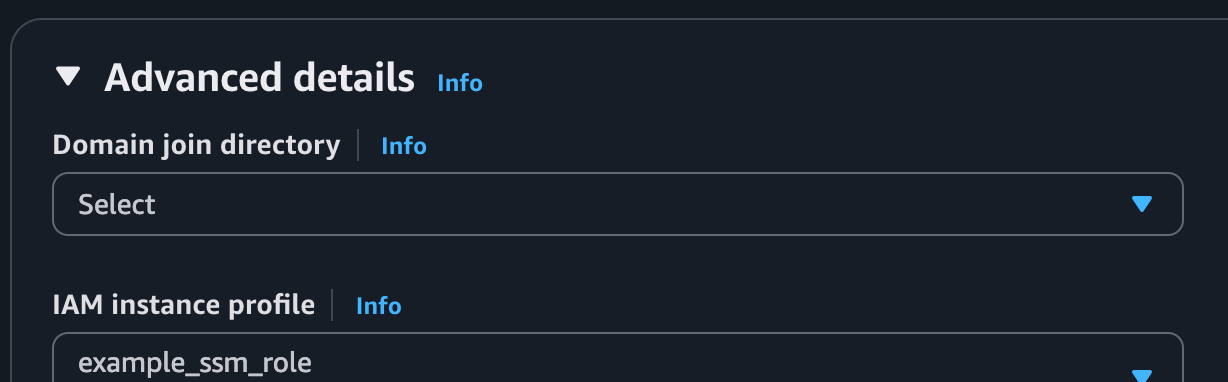
5. Connect to instance
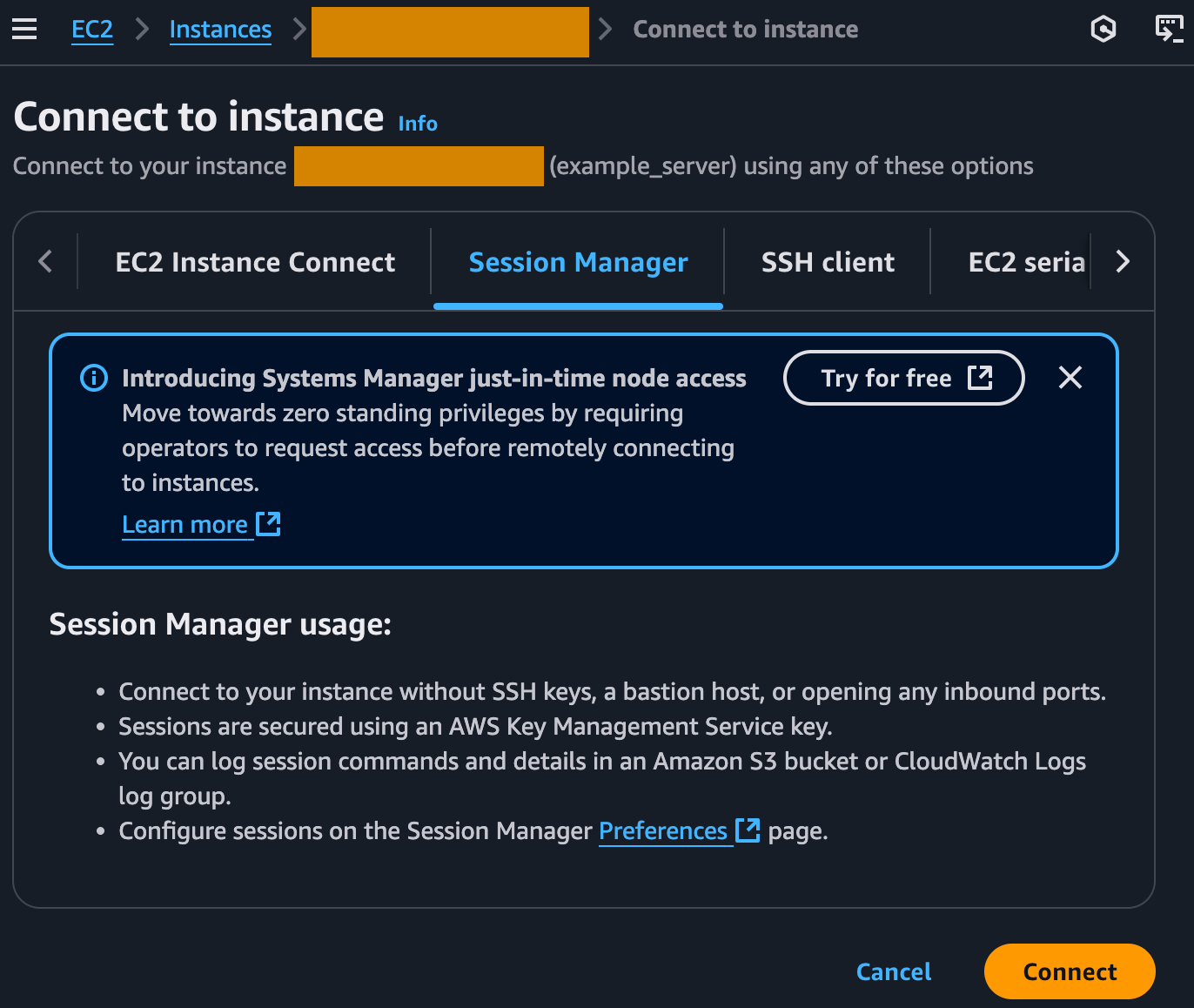
This will launch the shell of the EC2 instance and you can sign in normally. (Default if you chose Ubuntu as a quick start: `sudo su ubuntu`, or, for a more comprehensive list of default usernames for other Linux distros see the docs.)